Malunion Fractures: Causes, Treatment, and Optimal Healing
Malunion Fractures
Introduction
Fractures are common injuries, that can occur due to accidents, falls, or sports-related activities. While most fractures heal in the proper position with the right amount of medical attention and bones work correctly, sometimes, they don’t heal the way they should, and that’s when you get a bone malunion fracture. It’s like your bone is healing in a crooked or misaligned way. Understanding what bone malunion fractures are, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and recovery.
Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for Bone Malunion Fractures
Understanding malunion fractures is crucial because they cause ongoing pain and problems with movement if left untreated. Knowing what causes them, how to spot the symptoms, and what treatment options are available makes a big difference in how well you recover.
Bone Malunion Fracture Causes
The bone malunion fracture causes can vary, but some common factors are:
- Mis-alignment: If the broken bones are not set or aligned correctly during the initial treatment, they may heal in a misaligned position, leading to malunion. The chances of misalignment are higher if the fracture is near the joint areas like the wrist and ankles.
- Insufficient Immobilization: Improper immobilization of the fractured bone, such as not using a cast or splint can result in movement at the fracture malunion site, preventing proper healing and alignment.
- Delayed Treatment: Delayed or inadequate medical treatment following the fracture can contribute to malunion, as the bones may begin to heal incorrectly before proper realignment occurs.
- Severity of Injury: The severity of the initial injury, including the extent of bone displacement or fragmentation, can affect the occurrence of malunion.
- Poor Blood Supply: Inadequate blood supply to the fractured malunion area, often due to damage to blood vessels during the injury or surgical procedures, can impair the bone’s ability to heal properly.
- Infection: Infections at the site of the fracture malunion can interfere with the healing process, leading to complications such as delayed healing or malunion.
- Age and Health Factors: Factors such as advanced age, certain medical conditions (e.g., osteoporosis), and poor overall health can impair bone healing and increase the risk of malunion.
- Surgical Complications: In cases where surgical intervention is required to realign the bones, complications such as inadequate fixation or surgical errors can result in malunion.
Understanding these causes helps healthcare providers take appropriate measures to prevent malunion and promote optimal healing of fractures. These fractures can occur in different body parts, but one common area is the wrist, where bones may heal in a misaligned position, causing pain and limited mobility.
Bone Malunion Fracture Symptoms
How do you know if you have a bone malunion fracture? There are a few symptoms to watch out for. The malunion fracture symptoms can vary depending on factors such as the severity of misalignment and the specific location of the fracture malunion. However, common symptoms may include:
- Persistent Pain or Discomfort: Individuals with a malunion fracture may experience ongoing pain or discomfort at the site of the fracture, even after the initial healing period. This pain may increase by movement or pressure on the affected area.
- Visible Deformity: A malunion fracture can sometimes result in a visible deformity or abnormal appearance of the affected limb or joint. This may manifest as a visible bump, crookedness, or a bent compared to the uninjured side.
- Limited Range of Motion: Reduced flexibility or range of motion in the affected limb or joint is another common symptom of malunion fractures. Individuals may find it challenging to move the affected area as freely or comfortably as before the injury.
- Functional Impairment: Malunion fractures can interfere with daily activities and functional abilities, such as walking, gripping objects, or performing specific movements. Individuals may notice difficulty performing tasks that require the use of the affected limb or joint.
- Swelling or Tenderness: Swelling and tenderness at the site of the malunion fracture may occur, particularly during periods of increased activity or pressure on the affected area. The skin around the fracture malunion site may also feel warm to the touch.
- Instability or Weakness: Malunion fractures can lead to instability or weakness in the affected limb or joint, making it challenging to bear weight or maintain balance. This instability may increase the risk of falls or further injury.
- Functional Complications: Depending on the location and severity of the malunion fracture, individuals may experience functional complications such as difficulty in gripping objects or participating in sports or physical activities.
These symptoms can affect your daily life and need proper diagnosis from a healthcare provider.
Bone Malunion Fracture Diagnosis
Diagnosis of malunion fractures typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging tests to assess the alignment and healing of the fractured bone. Here’s an overview of the diagnostic process:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will perform a thorough physical examination of the affected limb or joint, assessing for signs of misalignment, deformity, swelling, tenderness, and functional impairment. They may also inquire about the circumstances of the injury and any symptoms experienced since the fracture occurred.
- Imaging Tests:
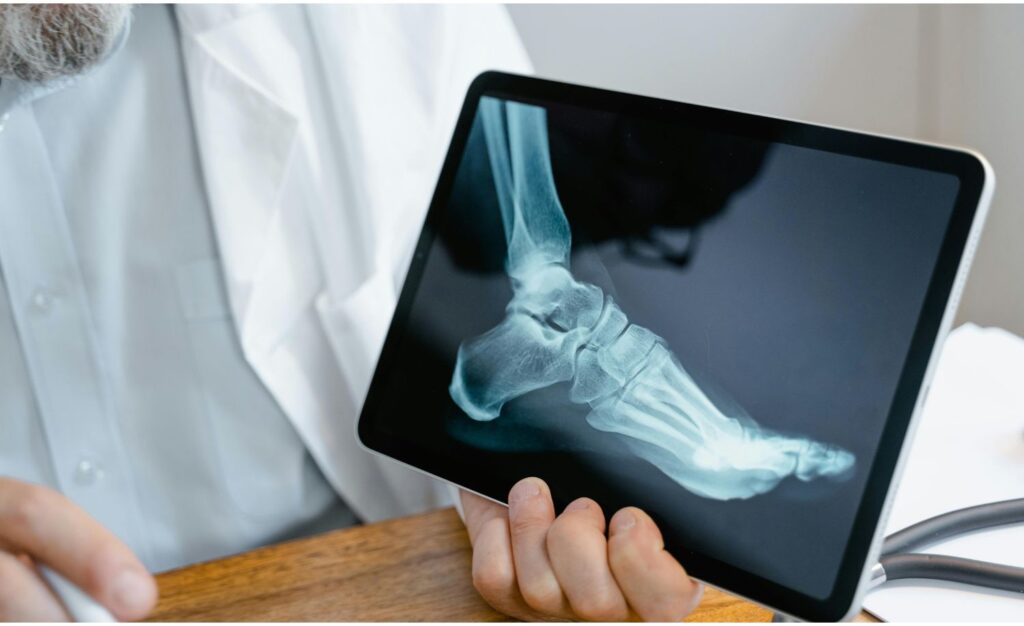
- X-rays: X-ray images visualize fractures and assess their alignment and healing progress. X-rays can reveal abnormalities such as malalignment, incomplete healing, or bone resorption.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the fractured bone, allowing for a more comprehensive assessment of the extent of malunion, displacement, and any associated complications.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans evaluate soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, surrounding the fractured bone. MRI can help identify any additional injuries or complications that may contribute to the symptoms of malunion fractures.
- Functional Assessment: In addition to imaging tests, a healthcare provider may assess the functional status of the affected limb or joint, including range of motion, strength, stability, and functional limitations. Functional tests may help determine the impact of the malunion fracture on daily activities and quality of life.
- Medical History: A thorough review of the patient’s medical history, including previous injuries, medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors, may provide valuable insights into the underlying causes of the malunion fracture and inform treatment decisions.
Based on the findings of the diagnostic evaluation, a healthcare provider can make a definitive diagnosis of malunion fracture and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs. Treatment options may include conservative measures such as immobilization with casts or splints, physical therapy, or surgical intervention to realign the bone and promote proper healing. Regular follow-up evaluations may be necessary to monitor progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure optimal outcomes.
Treatment for Malunion Fracture

A person with a bone fracture is given an immobilizer
When dealing with a malunion fracture, the goal of treatment is to realign the bone and restore its function. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the misalignment and other factors. Here, we’ll explore conservative approaches and surgical interventions commonly used to treat malunion fractures.
Conservative Approaches:
Immobilization with Casts or Splints: One of the primary methods to treat malunion fractures is immobilization with casts or splints. These devices help stabilize the affected limb, preventing further misalignment and allowing the bone to heal properly. By restricting movement, casts or splints promote the formation of new bone tissue in the correct position.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Exercises: Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises play a crucial role in the recovery process for malunion fractures. These exercises improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected limb. By targeting specific muscle groups and joints, physical therapy helps restore function and mobility, reducing pain and discomfort associated with the malunion fracture.
Pain Management Techniques: Pain management is an essential part of treatment for malunion fracture, especially during the early stages of recovery. Pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen, may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort. Additionally, techniques such as icing the affected area and using heat therapy can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Surgical Interventions:
Osteotomy to Realign the Bone: In cases where conservative approaches are ineffective or, the misalignment is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Osteotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting the bone to realign it properly. During the procedure, the surgeon carefully adjusts the position of the bone to restore proper alignment and function.
- Internal Fixation with Plates, Screws, or Pins: Internal fixation involves using metal implants such as plates, screws, or pins to hold the fractured bone in place while it heals. These implants provide support and stability to the bone, allowing for optimal healing. Types of internal fixation devices depend on the location and severity of the malunion fracture.
- External Fixation Devices: External fixation devices are another surgical option for treating malunion fractures. These devices consist of metal rods or pins attached to the outside of the affected limb, stabilizing the bone from the outside. External fixation devices are often used in cases where internal fixation is not feasible or as a temporary measure before definitive surgical intervention.
- Bone Grafting for Severe Cases: In severe cases of malunion fractures where there is significant bone loss or damage, bone grafting may be necessary to promote healing. During a bone grafting procedure, bone tissue is taken from another part of the body or a donor and transplanted to the fracture site. This helps stimulate new bone growth and facilitates the healing process.
Post-Malunion Treatment Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is a crucial phase of recovery after experiencing a malunion fracture. It promotes optimal recovery and restoring function to the affected limb or joint. Here are several reasons why post-malunion treatment rehabilitation is essential:
- Restoring Strength and Mobility: Rehabilitation exercises and therapies gradually strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and restore the range of motion in the affected limb or joint. This helps individuals regain the ability to perform daily activities and functional tasks efficiently.
- Preventing Muscle Weakness and Atrophy: Immobilization of the affected limb during the healing process can lead to muscle weakness and atrophy. Rehabilitation exercises target specific muscle groups to prevent muscle loss and promote muscle strength and endurance.
- Improving Functional Abilities: Rehabilitation aims to improve functional abilities such as walking, standing, reaching, and gripping objects. Through targeted exercises and activities, individuals learn how to perform these tasks safely and effectively, maximizing their independence and quality of life.
- Managing Pain and Discomfort: Rehabilitation techniques such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities like heat and cold therapy can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with the malunion fracture. By addressing pain symptoms, rehabilitation enables individuals to participate more fully in their recovery process.
- Enhancing Balance and Stability: Malunion fractures can affect balance and stability, increasing the risk of falls and further injury. Rehabilitation exercises focus on improving balance, coordination, and proprioception (awareness of body position), reducing the risk of falls, and improving overall stability.
- Facilitating Adaptation and Compensation: In cases where the malunion fracture results in permanent limitations or disabilities, rehabilitation helps individuals adapt to their new circumstances and develop compensatory strategies to perform daily activities more effectively. This may involve the use of assistive devices or modifications to the environment.
- Promoting Psychological Well-being: Coping with a malunion fracture can be challenging emotionally and psychologically. Rehabilitation provides a supportive environment where individuals receive encouragement, education, and guidance to cope with the physical and emotional aspects of their injury. This improves mood, confidence, and overall well-being during the recovery process.
- Preventing Secondary Complications: Malunion fractures can increase the risk of secondary complications such as stiffness, arthritis, and chronic pain. Rehabilitation helps mitigate these risks by promoting proper healing, maintaining joint mobility, and addressing any underlying issues that may contribute to complications.
Post-malunion treatment rehabilitation is essential for maximizing recovery outcomes, restoring function, and enhancing quality of life following a malunion fracture. These rehabilitation programs can be tailored to individual needs to regain independence in daily activities faster.
Duration of Recovery and Expected Outcomes
The duration of recovery from a malunion fracture can vary depending on various factors, including the severity of the fracture, the chosen malunion treatment approach, and individual factors such as age and overall health. In general, rehabilitation may begin soon after the fracture has been stabilized, but the full recovery process may take weeks to months.
During the rehabilitation process, individuals can expect to gradually progress in their abilities as they regain strength and mobility in the affected limb because new tender bone tissues are formed and they need time to become stronger. While some improvements may be noticeable early on, it’s essential to continue with rehabilitation exercises and therapies to achieve better outcomes over time.
Monitoring for Complications
While rehabilitation plays a vital role in promoting recovery, it’s also essential to monitor for potential complications that may arise following a malunion fracture. Some common complications include:
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the affected joint or limb can occur due to immobility during the healing process or as a result of scar tissue formation. Physical therapy exercises and stretching techniques can help alleviate stiffness and improve flexibility.
- Arthritis: Arthritis may develop in the affected joint over time due to changes in the joint structure or increased stress on the surrounding tissues. Monitoring for symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, and decreased range of motion is essential, as early intervention can help manage arthritis symptoms and prevent further deterioration.
- Chronic Pain: Chronic pain may persist following a malunion fracture, especially if there are underlying issues such as nerve damage or joint instability. Pain management techniques, such as medications, physical therapy modalities, and lifestyle modifications, may be necessary to help individuals cope with ongoing pain and improve their quality of life.
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring progress, addressing any concerns or complications that may arise, and adjusting the rehabilitation plan as needed. By staying proactive in rehabilitation and recovery efforts and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, individuals can maximize their chances of achieving a successful outcome and returning to their pre-injury level of function.
What is Nonunion, and how it's different from malunion:
Nonunion occurs when a broken bone fails to heal within the expected timeframe, typically within 6-9 months after the injury. However, malunion occurs when the bones heal in a misalignment manner.
- Causes of Nonunion: Nonunion can result from various factors, including poor blood supply to the fractured bone, infection, inadequate immobilization, or excessive movement of the affected limb.
- Symptoms of Nonunion: Symptoms may include persistent pain and tenderness at the fracture site, swelling, and limited mobility of the affected limb. In some cases, an open wound may be present if the bone protrudes through the skin.
- Diagnosis of Nonunion: Diagnosis is typically made through physical examination, imaging tests, and possibly additional diagnostic procedures such as bone scans or blood tests to assess bone healing and identify underlying causes.
- Treatments for Nonunion: Treatments may include surgical intervention to stimulate bone healing, such as bone grafting, fixation with metal implants, or the use of bone stimulation devices. In some cases, addressing underlying factors contributing to nonunion, such as infection or poor blood supply, may be necessary to promote healing.
Tips for Promoting Proper Bone Healing
A person with a malunion fracture is resting on bed
Proper bone healing is essential for fast recovery from fractures, ensuring the bone regains strength and function. Various factors influence the bone healing process, and understanding them is crucial for promoting optimal recovery.
- Nutrition for Bone Health: Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake is vital for bone formation and healing. Include foods rich in calcium and vitamin D in your daily diet, such as dairy products like milk, curd and cheese, millet like ragi, foxtail millet and finger millet, leafy greens like spinach and broccoli, and fish especially canned sardines. For those at risk of deficiency, dietary supplements can also be taken to support faster recovery of bone health.
- Hydration and Bone Healing: Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and bone healing. Aim for the recommended daily water intake to maintain optimal hydration levels, as dehydration can impair the bone healing process and delay recovery.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can delay the bone healing process. Smoking reduces blood flow to the bones, leading to delayed healing, while excessive alcohol intake can decrease bone density and impair the healing process. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can significantly improve bone health and promote faster healing.
- Proper Immobilization and Rest: Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for immobilization, such as wearing casts or splints, to ensure proper alignment and support for the healing bone. Avoid activities that stress the injured area and prioritize rest to allow the bone to heal effectively.
- Physical Activity and Rehabilitation: Gentle exercises and physical therapy play a crucial role in promoting bone healing and restoring function. Your healthcare provider may recommend specific exercises tailored to your condition and stage of healing. Gradually increase your activity level under their guidance to avoid overexertion and facilitate optimal recovery.
- Managing Chronic Conditions: Chronic conditions such as diabetes and osteoporosis can affect bone healing. It’s essential to manage these conditions effectively through medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring. Consultation with your healthcare provider is key to developing appropriate management strategies to support bone healing.
- Following Healthcare Provider’s Recommendations: Attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider and adhere to your treatment plan as recommended. Open communication with them is essential for addressing any concerns or complications that may arise during the healing process. Following their guidance ensures you receive the best care and support for optimal bone healing.
Prioritizing bone health and following these tips can significantly promote proper bone healing and enhance your recovery from fractures. You can accelerate the healing process and regain function more effectively by taking proactive steps to support bone healing.
Conclusion
Dealing with a malunion fracture can be frustrating, but understanding what it is and how to treat it is the first step toward recovery. Whether you need surgery or can manage without it, the most important thing is to get the right treatment at the right time. If you suspect you may have malunion or nonunion, it’s crucial to seek medical attention for evaluation and appropriate treatment for malunion fracture. Healthcare professionals can help you with the best way to get back on track and feel like yourself again.
Read Our Other Health Related Blogs
- How to Choose The Best Insulin Pumps For Diabetes Management
- Relax and Restore: Gentle Chair Yoga for Seniors PDF Edition
- Diabetes and Heart Disease: A Holistic Approach to Wellness
Cooking with Foxtail Millet Flour: Delicious and Nutritious Dishes
- Owala Water Bottle Challenge: Can You Drink More Water Today?
About The Author

1 thought on “Malunion Fractures: Causes, Treatment, and Optimal Healing”
facebook account sale account market account selling service